Casting director Lucy Pardee lifts the lid on her latest project, Lollipop, and working in the casting industry.
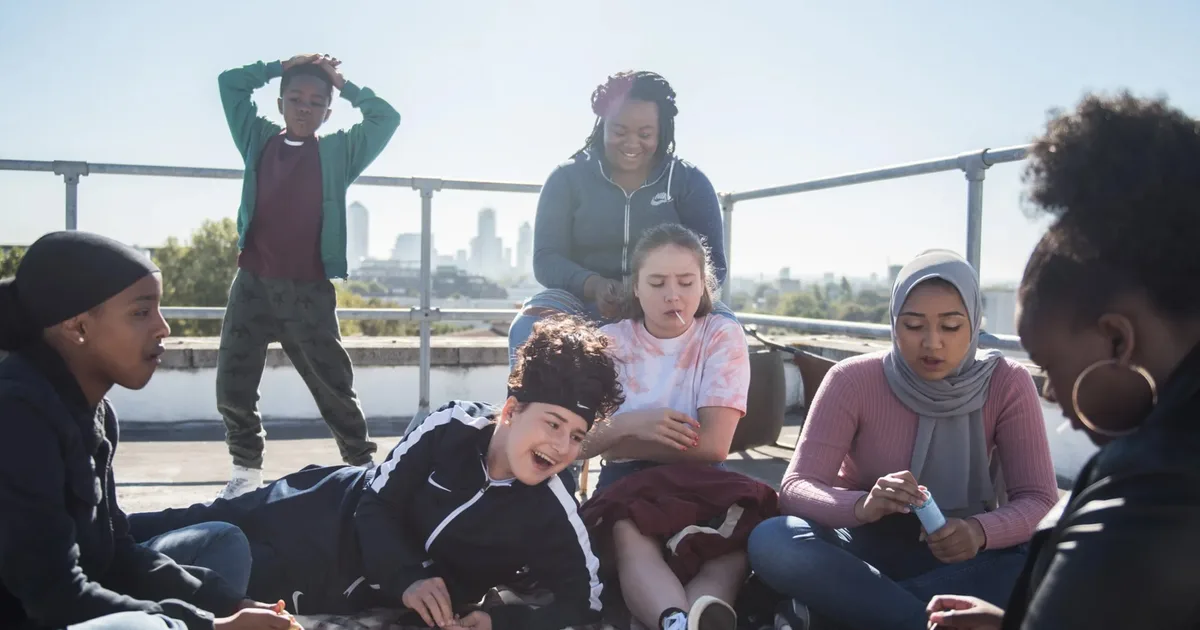
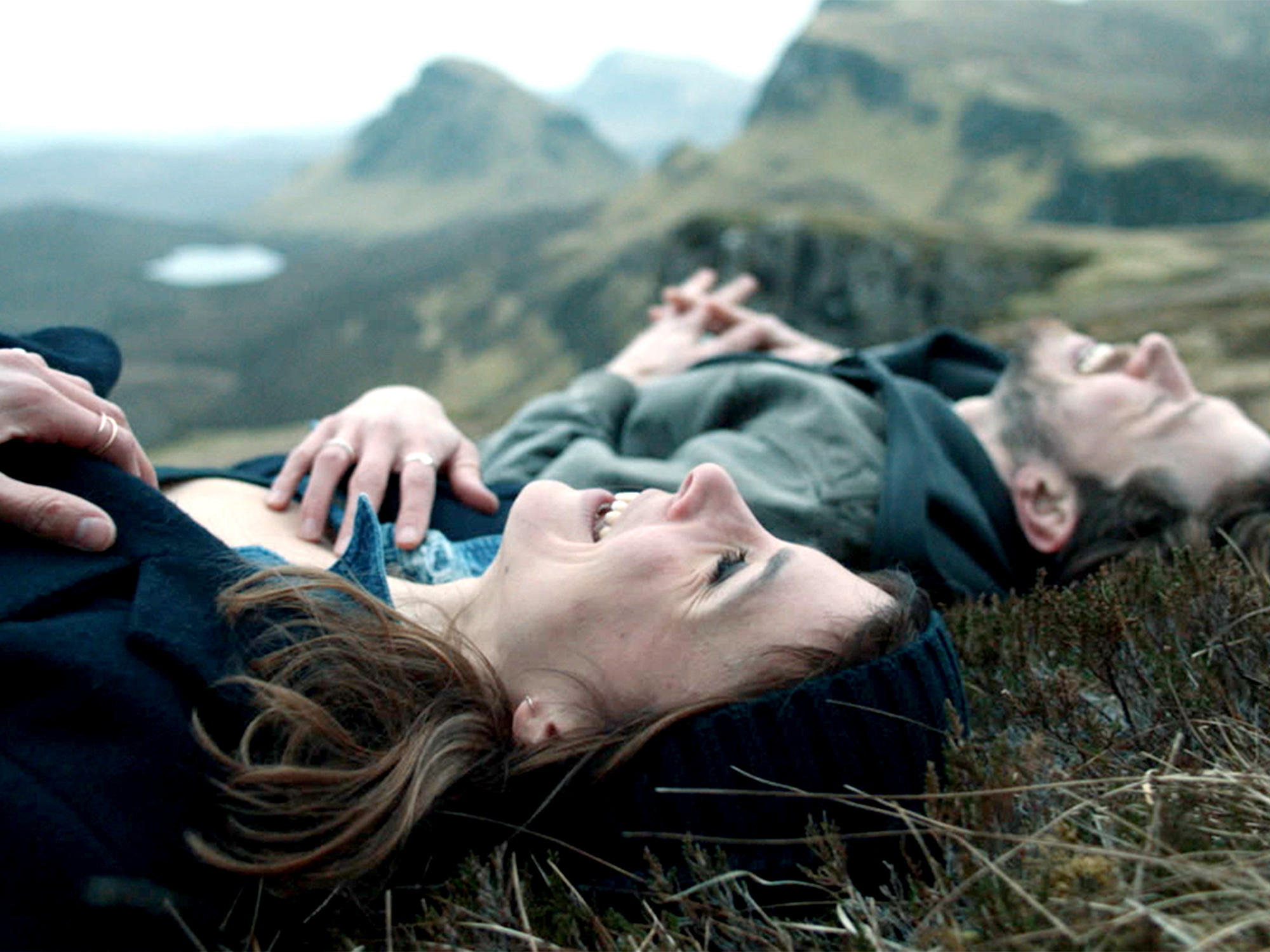
In Rocks, a teenage girl struggles to care for her little brother after being abandoned by her mother; In Bird, a young girl seeks magical adventure away from her unpredictable father; In Aftersun, a young girl’s father-daughter holiday comes to hold melancholy meaning. These moving, character-focused recent films share one thing: they were cast by Lucy Pardee. The BAFTA-winning casting director has worked with some of the UK’s finest directing talent, from Andrea Arnold to Jonathan Glazer to Lynne Ramsay, discovered countless homegrown stars and had decades of industry insight dedicated to widening diversity on the big screen.
Pardee’s careful casting has paid off since her first casting director credit with Arnold’s Wuthering Heights to her most recent film, Daisy-May Hudson’s feature debut, Lollipop. The poignant drama follows single mother Molly (Posey Sterling), fresh out of prison, trying to regain custody of her children but unable to while she’s homeless. It’s a piercing narrative that required a skilled cast. Demystifying the casting process, Pardee notes that finding the right actors is completely different with every project, but with Lollipop, the focus was connection and authenticity. “Because Daisy-May’s a documentary filmmaker, meeting people is really important,” Pardee explains. “She’s rather alternative. She wanted to bring a candle to light, but I said no, so instead she brought scents to neutralise the energy.”
Pardee shares that this interest in actors with lived experience is where street casting comes in. “There’s a real misconception that we just wander up to people,” Pardee clarifies. “Sometimes we do, but street casting is impossible without contacts with organisations because they will help us translate opportunities for the groups of people they work with.” Pardee’s experience working with theatre companies Clean Break (an organisation illuminating the stories of women in prison) and Cardboard Citizens (the UK’s only homeless people’s professional theatre company) informed Lollipop’s outreach. Pardee says the very purpose of this approach is “about making the ramp into the room accessible to people without previous acting experience.”
Lollipop embodies this outreach. For instance, TerriAnn Cousins, who plays Molly’s mother, came through Clean Break when Pardee previously cast her in Silver Haze. Also, Idil Ahmed, who plays Molly’s supportive childhood friend Amina, joined Lollipop through an organisation that works with East African and Somali communities after seeing Kosar Ali, an actor of Somali descent, star in Rocks. “I felt incredibly proud that we could bridge Kosar into the industry with Rocks,” Pardee said. “Idil and her four children are huge fans of Rocks. She was one of the people making a connection; Idil had never acted before, but felt like this was an opportunity she could step into because someone else had.”
Despite these connections and having a slate of exciting projects, Pardee highlights that she remains concerned about the shrinking space for newcomers in the industry. “There’s a real insecurity at the moment in terms of projects being seen,” Pardee shares, adding that there’s added pressure on casting directors to work with actors with profiles, the antithesis of independent film as “a crucible for launching talent.” In response to this industry-wide insecurity in the arts, Pardee co-founded and serves as an advisor for We Are Bridge, an industry body committed to supporting “people who have come into the industry through alternative pathways, bridging to their next opportunities.” It’s not just allowing an actor a first role, but helping them secure a second.

This work surrounding industry access is not just based on anecdotal experience; less than 10% of film and TV workers are from working-class backgrounds, the lowest in a decade, according to Channel 4’s 2024 report. Pardee says progression towards diverse working-class representation is “not a cultural shift to the future, but it’s almost a cultural shift to the past… [the UK] has a tradition of working class representation; we’re not breaking boundaries that haven’t been broken before, we’ve neglected pathways. Austerity kicked the shit out of those pathways which started with dramas in schools and youthclubs and access at community level.”
Pardee cites Adolescence as an interesting example, as much of the young cast came from grassroots drama organisations. However, these programs aren’t free to access. “There’s a whole wave of talent that, as soon as you put a price on it, isn’t able to do it,” Pardee notes. “Privilege does not equal talent.” This barrier to entry is not only harming the industry but also the quality of independent film.
This investment in the next generation is also clear in several recent films Pardee has worked on (Lollipop, Bird and Aftersun), which see her tasked with finding children and young people who can handle emotionally mature scenes. Exemplifying this, Luke Howitt and Tegan-Mia Stanley Rhoads deliver fantastic performances as Molly’s children in Lollipop. Rhoads is particularly impressive as she sobs and pleads for her mother to obey the rules to regain custody of them. Pardee explains that reaching such emotions is built around fictional play and imagination; there’s an end goal, but the journey to that point is up to each actor.
There has been a recent dialogue about social media followers dictating who gets into the casting room when it comes to casting young people. “Not in my world!” Pardee laughs, remarking social media is a double-edged sword: though it has unlocked a door for accessibility, an over-reliance has led to a “generation of people who will send a self-tape based on, I think, how they look.” Pardee emphasises that self-tapes will never replace auditioning in the room, which is a safe space for failure and imperfection: “I don’t know whether it’s COVID or social media, but there’s definitely risk aversion in the younger people coming through. In art, you must be able to take a swing, miss, and feel ok to take another one.”

Pardee’s upcoming slate includes much-anticipated projects, including Lynne Ramsay’s psychological portrait Die, My Love, starring Robert Pattinson and Jennifer Lawrence. “We found Robert in a Greggs,” Pardee laughs. “I’ve been working with [Ramsay] for quite a long time, but this is the first time we’ve cast a feature film together. She creates such a ripe, safe environment. I think that’s why we all do some of our best work with her, because of this safety.” Pardee is also in the “very, very early days” of casting How to Have Sex writer-director Molly Manning Walker’s A24 show about girls’ football. Pardee notes she’s conducting a lot of outreach and that authentic representation is a core focus for this casting. “If you want to represent a story authentically, I believe in: ‘nothing about us without us’. Because Molly is part of this community, it’s so exciting.”
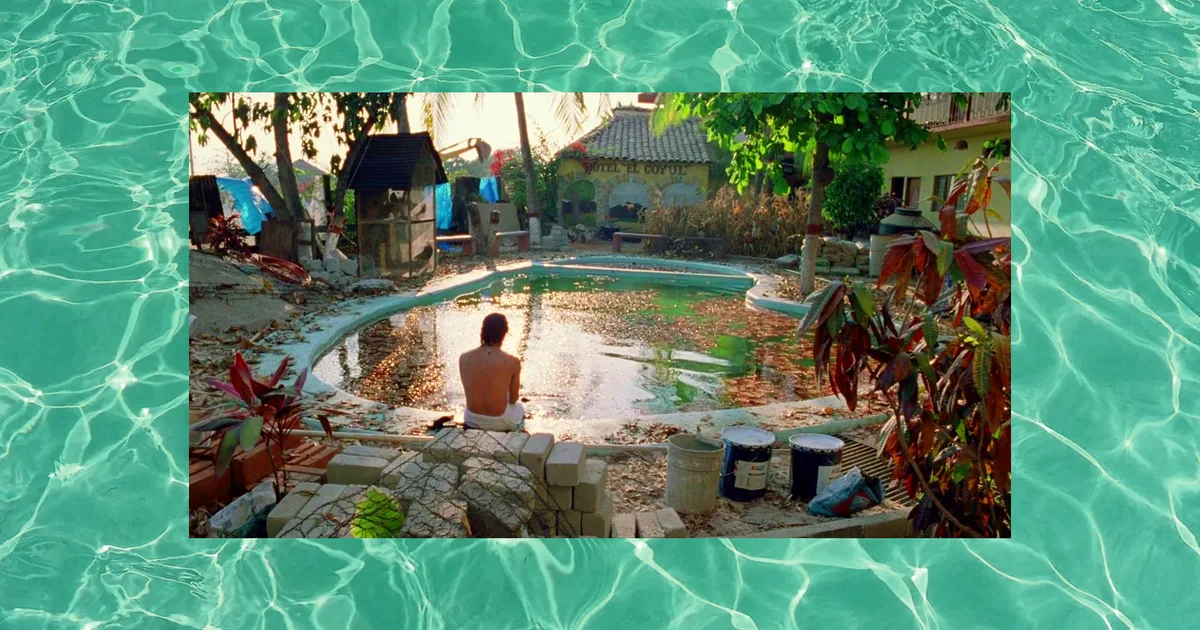
Many stars have passed through Pardee’s casting process, but one of her most memorable was Aftersun’s Francesca Corio. Corio beat out 900 applications to star in Charlotte Wells’ heartbreaking film, opposite Paul Mescal. Pardee remembers auditioning 16 girls in a snow-covered, empty wedding venue in Glasgow in 2021 with Welles and producer Adele Romanski. Pardee recalls the special moment: she acted opposite Corio as her mother, and the young actress had to reach a point of sadness. “She was so genuinely sad, I got this feeling of ‘we’ve found her!’ It was profound,” Pardee recalled. “I asked her, ‘What were you thinking about?’ She said her guinea pig is about to die. The next day we tentatively asked about her guinea pig. Frankie said: ‘My guinea pig died, but it’s ok, my mum brought me a chip supper. So I’m fine… let’s act!’”